Understanding ADCC Assay with Cro: A Comprehensive Guide
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) is a crucial mechanism by which antibodies can enhance the immune response against pathogens. The ADCC assay is a laboratory technique used to measure the efficacy of antibodies in activating immune cells to kill target cells. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the ADCC assay, focusing on the role of Cro, a key component in this process.
What is ADCC?
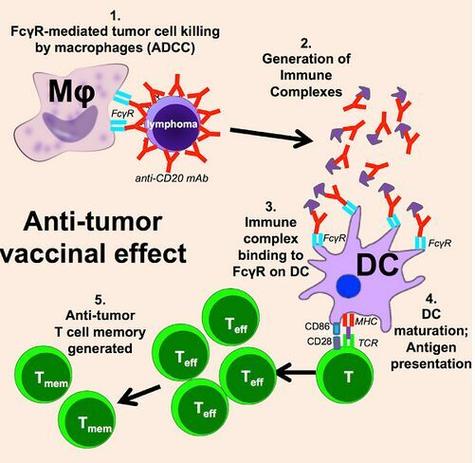
ADCC is a process where antibodies bind to the surface of target cells, such as cancer cells or virus-infected cells, and recruit immune cells, like natural killer (NK) cells, to destroy these cells. This mechanism is particularly important in the context of cancer immunotherapy, where monoclonal antibodies are used to target and eliminate tumor cells.
![]()
The ADCC Assay: A Method to Measure ADCC Activity
The ADCC assay is a standardized test that measures the ability of an antibody to induce cell death in target cells through ADCC. This assay is essential for evaluating the potential of therapeutic antibodies in clinical settings. The following steps outline the general procedure for conducting an ADCC assay:
-
Target cells are labeled with a dye that becomes fluorescent upon cell death.
-
Antibodies are added to the mixture, allowing them to bind to the target cells.
-
Immune cells, such as NK cells, are added to the mixture, where they can recognize and kill the antibody-bound target cells.
-
The mixture is incubated for a specific period, allowing the ADCC process to occur.
-
The fluorescence of the dye is measured, which correlates with the number of target cells killed by the immune cells.
The Role of Cro in ADCC
Cro is a protein that plays a critical role in the ADCC process. It is a member of the Fc纬 receptor family, which is responsible for recognizing the Fc region of antibodies. When an antibody binds to a target cell, Cro can bind to the Fc region of the antibody, leading to the activation of immune cells. Here’s how Cro contributes to ADCC:
-
Recruitment of Immune Cells: Cro binds to the Fc region of the antibody, which allows immune cells, such as NK cells, to recognize and bind to the target cell.
-
Signal Transduction: Binding of Cro to the Fc region of the antibody triggers a signaling cascade within the immune cell, leading to the activation of cytotoxic mechanisms.
-
Enhanced Cytotoxicity: The activation of immune cells by Cro results in increased ADCC activity, leading to more efficient killing of target cells.
Table: ADCC Assay Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Target Cells | Cells that express the antigen of interest, such as cancer cells or virus-infected cells. |
| Antibodies | Monoclonal antibodies that bind to the antigen on the target cells. |
| Immune Cells | Cells, such as NK cells, that can recognize and kill the antibody-bound target cells. |
| Incubation Time | The duration of time the mixture of target cells, antibodies, and immune cells is incubated to allow the ADCC process to occur. |
| Fluorescence Measurement | The measurement of the fluorescence of the dye that becomes fluorescent upon cell death, which correlates with the number of target cells killed by the immune cells. |
Applications of ADCC Assay with Cro
The ADCC assay with Cro has several applications in the field of immunotherapy:
-
Drug Development: The ADCC assay is used to evaluate the efficacy of therapeutic antibodies in preclinical and clinical studies.
-
Target Selection












